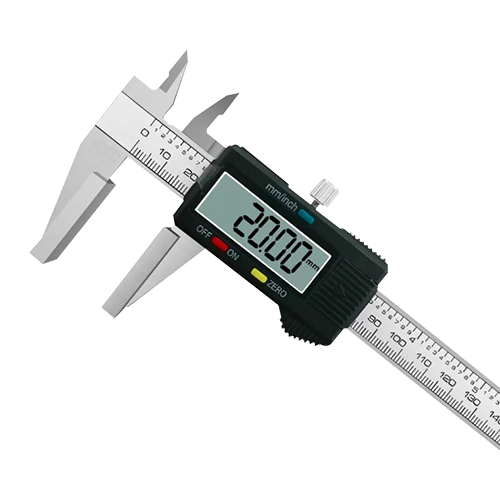
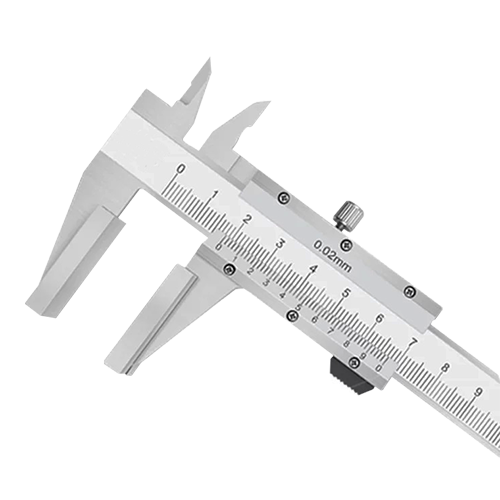
A vernier caliper is a precision tool for measuring length, inner and outer diameters, and depth. It has a simple structure, is easy to use, offers moderate accuracy, and has a wide measuring range. It consists of a main scale and a vernier scale. The main scale is fixed, while the vernier scale is movable. Different measuring needs are achieved through two pairs of measuring jaws (inner and outer measuring jaws).
Main Scale: Fixed part, minimum division 1 mm.
Vernier Scale: Movable part, graduation value determines accuracy (e.g., 0.02 mm, 0.05 mm).
Measuring Jaws: Outer measuring jaws measure outer diameter, inner measuring jaws measure inner diameter, and the depth gauge measures depth.
Check Zero Point: Close the measuring jaws; the vernier scale and main scale zero mark should be aligned.
Measure Outer Diameter: Hold the object in the outer measuring jaws and tighten the screws to prevent movement.
Measure Inner Diameter: Support the hole with the inner measuring jaws and gently pull to ensure it is flush against the inner wall.
Measure Depth: With the bottom of the measuring jaw flush against the surface, push the depth gauge to the bottom of the groove.
Integer Part: The nearest graduation on the main scale to the left of the vernier zero line.
Decimal Part: Alignment number × graduation value (e.g., 0.02mm).
Example: Main scale 64mm, vernier 9th line aligned, reading 64.18mm.
Handle with care: Avoid collisions or drops.
Cleaning and maintenance: Keep the measuring surface clean and avoid storing with cutting tools.
Environmental requirements: Store in a dry, neutral place, away from acidic or alkaline substances.